IEC/ISO 27001 Importance, Advantages, and Process.
Information is a critical asset for organizations in today's digital age. Protecting confidential information is of utmost importance to avoid reputational damage, legal implications, and financial loss. The ISO 27001 standard provides a framework for organizations to implement an Information Security Management System (ISMS) to protect their information assets. In this blog, we will discuss the importance, advantages, and the process of obtaining the ISO 27001 certification and also how it is different from SOC2
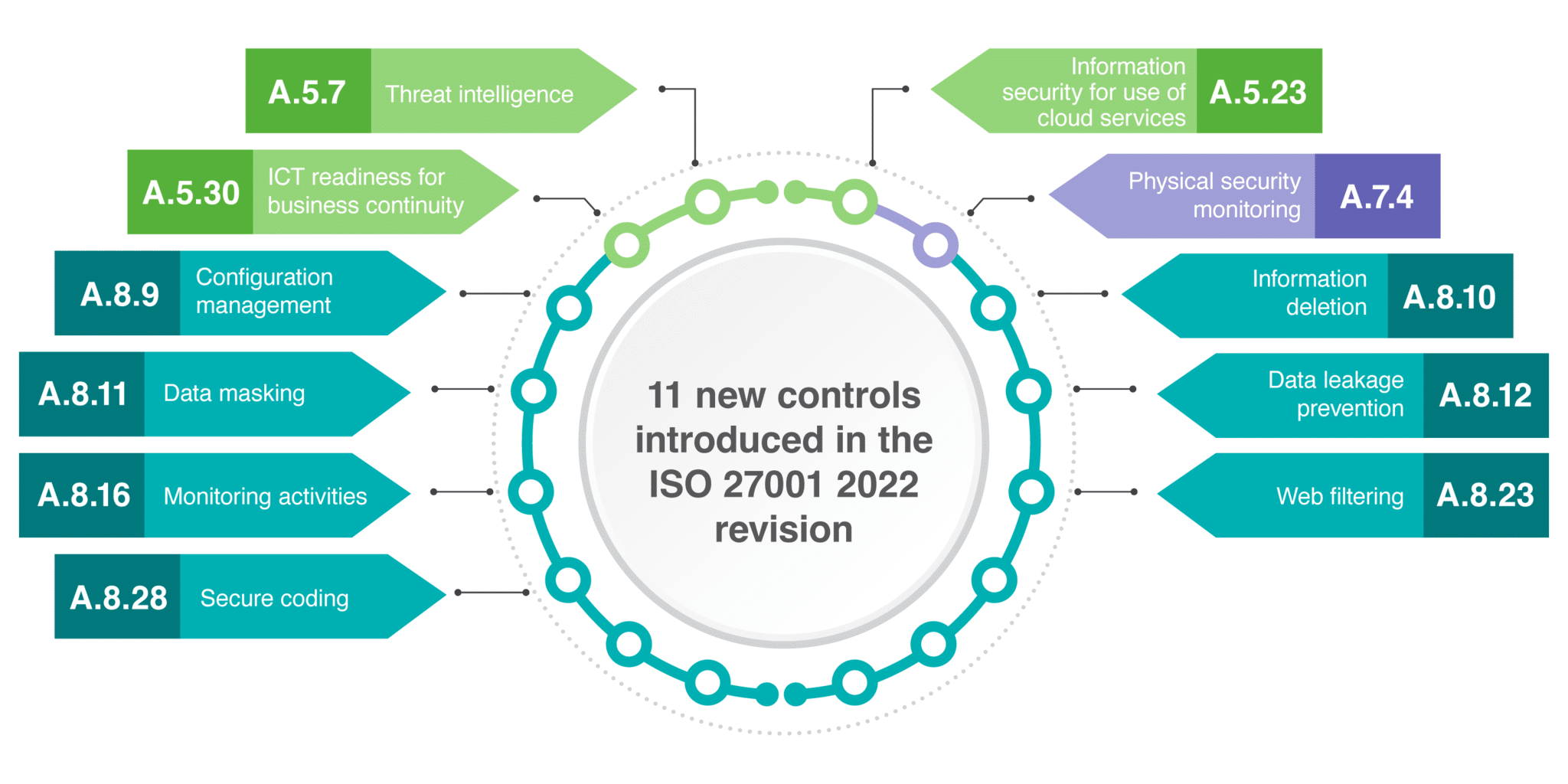
Importance of ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is essential for any organization that handles sensitive information, including financial data, intellectual property, and personal data. It provides a systematic approach to managing information security risks and ensures that organizations implement appropriate measures to protect against threats. By implementing ISO 27001, organizations can improve their information security posture and protect their reputation.
Advantages of ISO 27001 Certification
There are several advantages to obtaining ISO 27001 certification, including:
- Increased Credibility: ISO 27001 is a globally recognized standard, and certification demonstrates that an organization has implemented an effective ISMS. This can increase the organization's credibility and enhance its reputation.
- Competitive Advantage: ISO 27001 certification can give an organization a competitive advantage over its competitors. It can demonstrate to customers and partners that the organization takes information security seriously and is committed to protecting their data.
- Legal Compliance: ISO 27001 certification can help organizations comply with various laws and regulations related to information security, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
- Risk Management: Implementing ISO 27001 helps organizations identify and manage information security risks. It provides a systematic approach to risk management, enabling organizations to make informed decisions about risk mitigation.
- Continuous Improvement: ISO 27001 requires organizations to continually monitor and improve their information security management system. This helps organizations stay up to date with evolving security threats and best practices.
Process of Obtaining ISO 27001 Certification
The process of obtaining ISO 27001 certification involves the following steps:
- Gap Analysis: Conduct a gap analysis to identify the organization's current information security management practices and identify areas that need improvement.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a risk assessment to identify and assess information security risks and determine appropriate risk mitigation measures.
- ISMS Development: Develop and implement an Information Security Management System (ISMS) that aligns with ISO 27001 requirements.
- Internal Audit: Conduct an internal audit to ensure that the ISMS is effectively implemented and maintained.
- Certification Audit: Engage an accredited certification body to conduct a certification audit. The certification body will verify that the organization's ISMS meets ISO 27001 requirements.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously monitor and improve the ISMS to ensure that it remains effective and up to date.
Difference between ISO27001 and SOC 2
ISO 27001 and SOC 2 are both standards related to information security, but they have different scopes and focus areas.
ISO 27001 is a standard that provides a framework for implementing an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It is a globally recognized standard that focuses on the management of information security risks and the protection of sensitive information. ISO 27001 is applicable to any organization that wants to implement an ISMS, regardless of the size or industry.
SOC 2, on the other hand, is a set of guidelines and criteria developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) to assess the controls and processes of service organizations that handle customer data. It is specifically designed for service organizations that provide services such as cloud computing, data processing, and software as a service (SaaS).
The SOC 2 framework has five trust principles - security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy - that organizations must demonstrate they are meeting. SOC 2 reports are issued by independent auditors after they have assessed an organization's controls against these principles.
There are a few differences between ISO 27001 and SOC 2 that service organizations should consider when choosing a framework:
- Scope: ISO 27001 is a broader standard that covers all aspects of information security management, while SOC 2 focuses specifically on the controls related to the five trust principles - security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
- Audit Approach: The audit approach for ISO 27001 and SOC 2 is different. ISO 27001 certification requires a third-party audit to verify that the organization has implemented an effective ISMS, while SOC 2 requires a SOC 2 audit report from an independent auditor that verifies that the organization has implemented controls that meet the trust principles.
- Geographic Scope: While both standards are recognized globally, SOC 2 is more commonly used in North America, while ISO 27001 is more widely recognized in Europe and Asia.
Ultimately, the choice between ISO 27001 and SOC 2 depends on the organization's needs and objectives. ISO 27001 is a comprehensive standard that can be used to demonstrate an organization's commitment to information security, while SOC 2 provides a specific set of guidelines for assessing the controls of service organizations. Service organizations should evaluate their specific needs and objectives before deciding which standard to pursue.
A service organization can choose ISO 27001 instead of SOC 2 to demonstrate its information security practices.
While SOC 2 is a widely recognized framework for service organizations, it is not the only option available. ISO 27001 is a globally recognized standard that provides a framework for implementing an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It is applicable to any organization, regardless of size or industry, and can be used to demonstrate an organization's commitment to information security.
There are a few differences between ISO 27001 and SOC 2 that service organizations should consider when choosing a framework:
- Scope: ISO 27001 is a broader standard that covers all aspects of information security management, while SOC 2 focuses specifically on the controls related to the five trust principles - security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
- Audit Approach: The audit approach for ISO 27001 and SOC 2 is different. ISO 27001 certification requires a third-party audit to verify that the organization has implemented an effective ISMS, while SOC 2 requires a SOC 2 audit report from an independent auditor that verifies that the organization has implemented controls that meet the trust principles.
- Geographic Scope: While both standards are recognized globally, SOC 2 is more commonly used in North America, while ISO 27001 is more widely recognized in Europe and Asia.
Ultimately, the choice between ISO 27001 and SOC 2 depends on the organization's needs and objectives. ISO 27001 is a comprehensive standard that can be used to demonstrate an organization's commitment to information security, while SOC 2 provides a specific set of guidelines for assessing the controls of service organizations. Service organizations should evaluate their specific needs and objectives before deciding which standard to pursue.
